Payment card fraud is an ongoing major issue in the financial industry, causing substantial financial losses projected to reach 40 billion dollars by 2027. As the industry grows, detecting fraud patterns becomes inherently difficult, almost impossible to detect manually. This project tackles a fundamental question: can we teach machines to spot fraudulent transactions by showing them only what "normal" looks like? The modern approach relies on unsupervised machine learning studying highly imbalanced datasets to uncover patterns and outliers.
The Data Challenge
Working with Lopez-Rojas's PaySim dataset containing 6 million transactions across 11 features, the challenge was immediately apparent: only 0.13% of transactions were fraudulent. Finding fraud in this context truly becomes like searching for needles in haystacks. Rather than trying to define what fraud looks like (since criminals constantly adapt), I trained models on abundant "clean" data and tuned them to detect "novelties"—transactions that don't fit normal patterns.
Three Approaches to Digital Detective Work
I compared three unsupervised learning approaches:
- K-Means Clustering: Grouping normal transactions into clusters and flagging outliers
- Gaussian Mixture Models: Modeling normal transactions as probability distributions
- AutoEncoder Neural Networks: Training networks to reconstruct normal transactions, where high reconstruction error signals anomalous behavior
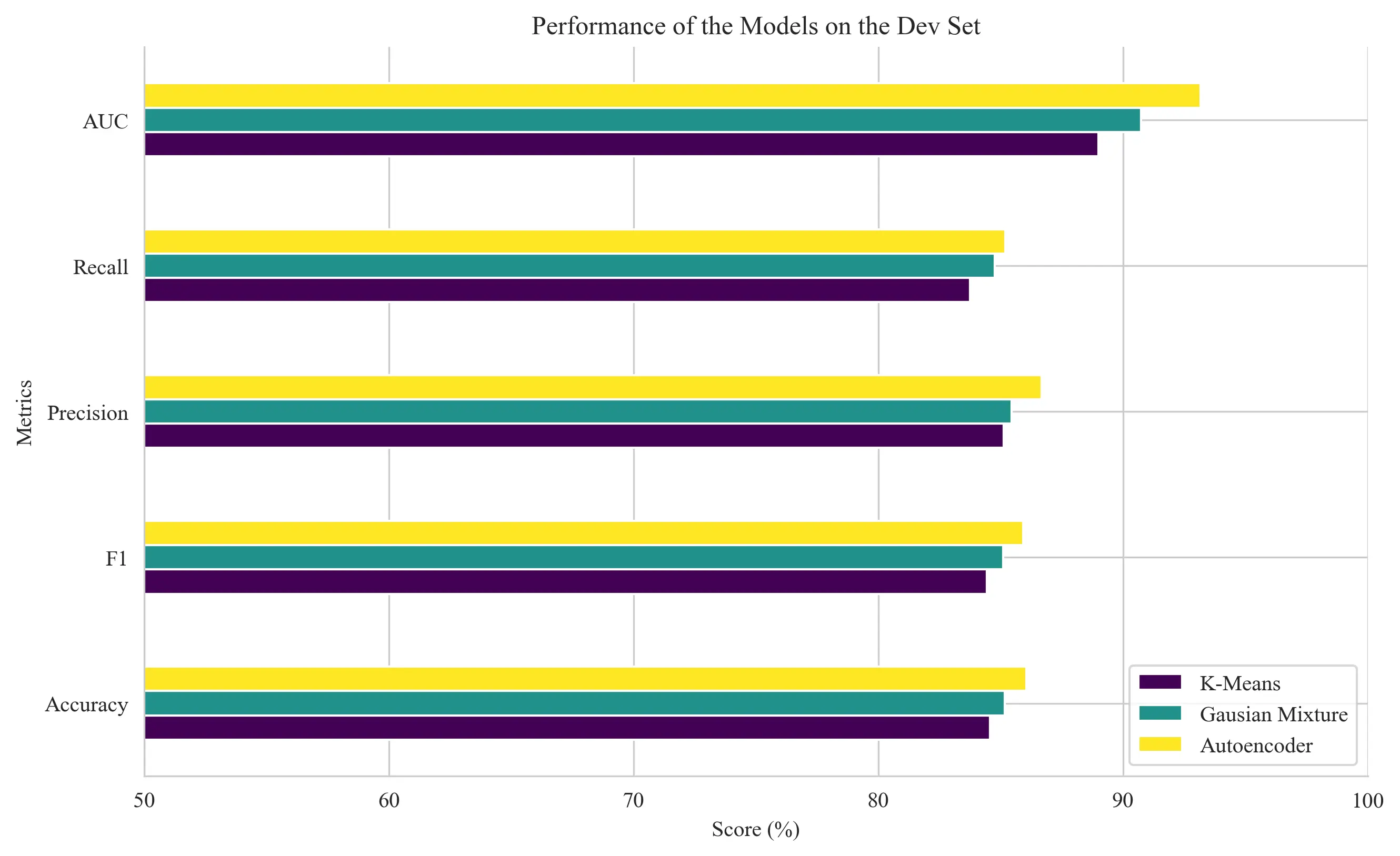
The AutoEncoder method outperformed the other approaches with an AUC of 0.93, demonstrating superior ability to distinguish between normal and fraudulent transactions through its capacity to capture non-linear relationships.
The Art of Balance
A critical aspect of fraud detection is finding the right balance between catching fraud and avoiding false alarms. The reconstruction threshold was carefully tuned to maximize the F1 score, achieving 0.86—ensuring we catch fraud without overwhelming customers with false alarms.
The AutoEncoder's automatic feature discovery outperformed hand-crafted features, revealing subtle transaction patterns that human domain expertise might miss, while training exclusively on legitimate transactions proved more effective than trying to learn from fraudulent examples.
The Ongoing Arms Race
This project highlighted that fraud detection is fundamentally an arms race between increasingly sophisticated detection methods and constantly adapting criminal tactics. The AutoEncoder's success represents a significant step forward, but the real challenge lies in building systems that can adapt and evolve alongside emerging threats.
Success in fraud detection requires balancing technical excellence with business practicality—protecting customers while maintaining seamless user experiences. The war against financial crime continues, and machine learning provides powerful weapons in this digital battlefield.